Machine Learning algorithms are one of the most important things to decide during model training and building. All the datasets and problem statements related to that in machine learning are not the same and can have different patterns and complexity. In such cases, selecting the best suitable machine learning algorithms becomes a significant step of model building.
This article will discuss the most popular machine learning algorithms’ PROs and CONs and the appropriate reason behind them. This knowledge will help one understand the problem statement better and select the best-fit algorithm for model building. This will also help one to answer interview questions related to PROs and CONs of Machine learning algorithms.
Table of Contents
- Linear Regression
- Decision Trees
- Support Vector Machines
- The Best Among Them?
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
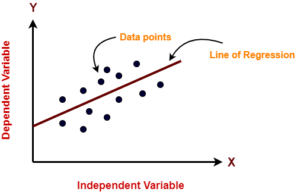
1. Linear Regression
In Linear Regression, the algorithm assumes the data to be linear and doe snot has multicollinearity. The algorithm simply calculates the slope and intercept for the best fit line and it can be used for classification and regression problems.
PROs:
1. Easy to Understand:
Linear regression is one of the simplest machine learning algorithms, which is easily understandable and straightforward to Implement. This algorithm can be adequately understood with simple linear algebra and statistics.
2. Regularization:
In this algorithm, the regularization techniques can be implemented in their respective loss function to handle the overfitting of the model.
3. Parametric Model:
Linear regression is a parametric machine learning algorithm that assumes some parameters and makes predictions. One of the famous assumptions is that the dataset should be linear to apply linear regression on that. If the proper liner dataset is given to its algorithm, then this algorithm performs exceptionally well on such datasets.
CONs:
1. Non-Linear Datasets:
As the linear regression assumes that the dataset should be linear, if nonlinear data is fed to this algorithm, it will perform more than ever.
2. Overfitting:
The linear regression is prone to overfitting, frequently overfitting the data.
3. Outliers:
If outliers are present in the dataset, then linear regression would be the poorest choice. Linear regression can not handle the dataset’s outliers, resulting in poor performance.
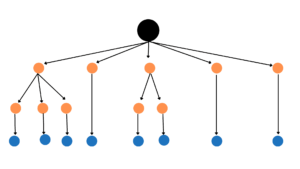
2. Decision Trees
In simple words, decision trees are the type of algorithm which is defined based on so many if-else conditions. It can be assumed as a whole tree having nodes and junctions where the data is split according to several parameters e.g entropy, information gain, etc.
PROs:
1. Visualize and Tuning:
Decision trees are one of the algorithms that can be easily visualized through several libraries and tuned according to that. One famous decision tree visualization library is dtreeviz, which can be used to visualize the decision tree correctly and with every model and condition of splitting the node.
2. Accuracy:
Decision Trees perform well on very high dimensional datasets and can be tuned if performs poorly; tuning some parameters, like the tree’s depth and splitting criteria, can enhance the tree’s performance.
3. Non-Linear data:
Unlike linear regression, decision trees perform well on linear and nonlinear datasets.
CONs:
1. Complexity:
Decision trees are the algorithm that might require so many hyperparameters to best fit on the given dataset. Because of that, the complexity of the algorithms becomes very high.
2. Overfitting and Underfitting:
If the tree depth of the decision tree is set to a very high value, then the tree can show overfitting behavior, and if the tree depth is shallow, the tree can show underfitting behavior. Here the tree depth should be the optimum value to achieve the best fit solution. The use of bagging algorithms like the random forest can handle such cases.
3. Data:
As the decision trees split the dataset based on some of the parameters of the given data, if there is a slight change made to the dataset, then all the splits will be of no use, and there will be a need for model training again from scratch.
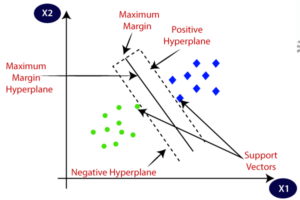
3. Support Vector Machines:
The support vector machine algorithms are the type of complex algorithms that have the regularization and classification cost function like Huber scores in its argmin and argmax function which are used to maximize the distance between positive and negative planes from the best fit line.
PROs:
1. Accuracy:
Support vector machines are machine learning algorithms that perform best on high-dimension data and give accurate results.
2. Non-Linear Data:
Support vector machines can perform best on nonlinear data as well. It acts as well as linear regression performing with linear data.
3. Limited Data:
Support vector machines are machine learning algorithms that do not require massive data to train. This algorithm performs well on limited or small amounts of data as well.
CONs:
1. Complexity:
Support vector machines are very complex to understand and implement. The working mechanism of the algorithms makes it very difficult; hence, it is one of the most complex algorithms of all time in machine learning.
2. Tuning:
There is a parameter called kernel size in the support vector machines, and the kernel size should be tuned well to get better performance from the support vector algorithms.
3. Performace on Large Data:
Support vector machines perform very poorly on a considerable amount of data. It gives the best results in small datasets and tends to perform very poorly on large amounts of datasets.
The Best Among Them?
Although there is no thumb rule to use any of the machine learning algorithms for all time, as all the problem statements and datasets related to the machine learning field are different and can have very different patterns and behavior, one cannot say the best-fit machine learning algorithm for the same initially. After carefully reviewing the data and reading the parameters, one can only estimate the probability of such algorithms that can perform better on the dataset. Based on the algorithm’s working mechanism and PROs and CONs, one can estimate the best suitable machine learning algorithm for the same.
Key Takeaways
- Linear regression performs well on linear data, it can not handle the outliers properly, and the regularization techniques can be easily implemented.
- Decision performs well on nonlinear data but is prone to minor changes in the dataset. It can overfit and underfit the data if not tuned well.
- Support vector machine is one of the complex algorithms in machine learning, which performs well on small and nonlinear datasets.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed some of the top-rated PROs and CONs of different machine-learning algorithms with the core intuition behind them. We also discussed the approach to select the best-fit algorithm initially for the given dataset and problem statement. Knowledge about these concepts will help one to understand and choose the best-fit algorithms for the problem statement. It will also help one to answer interview questions differentiating between them.