In machine learning to achieve higher accuracies and performance of the model, the data quality plays a major role while enhancing the model. If good quality data with meaningful features are provided to the machine learning model, then the model can be very accurate and reliable with lesser computational powers.
Principle Component Analysis, or PCA, is also one of the techniques that are used to enhance the quality of the data in terms of the dimensionality of the data. It is one of the famous dimensionality reduction techniques used in machine learning to reduce the dimensionality of the data and then the computational power needed to train the data.
In this article, we will discuss the principle component analysis, its working mechanism, its importance, and its application ns with good examples. This article will help one to understand the technique better and will be able to apply it if needed.
So, before directly diving into the principle component analysis, let us discuss the Curse of Dimensionality.
Table of Contents
- Curse of Dimensionality
- What is Principle Component Analysis?
- How Does PCA Works?
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
Curse of Dimensionality
In machine learning, majorly we have two types of features, independent features, and dependent features. Independent features are those that are independent of each other and which are used for model training, while dependent features are those which are target variable and which is to be predicted by the model.
Now sometimes we have a dataset with lots of features that can be also called dimensions. In such cases the computational power of the model becomes very high which causes the slowness of the model and sometimes, it can affect the quality and performance of the model too.
For example, we know that KNN is a distance-based algorithm that works on the principle of calculating the distances between points or data points. Now here, the computations will be very low if the dimension of the data is only two, but the computations become complex and time-consuming when the dimension increases.
Two dimensions: d = sqrt ((Y2 - Y1)^2 + (X2 - X1)^2)
Three Dimensions: d = sqrt ((Z2 - Z1)^2 + (Y2 - Y1)^2 + (X2 - X1)^2)
We noticed in the example that the computational power increases with the dimensions of the dataset which can be considered as the curse for the model and its performance, which phenomenon is known as the curse of dimensionality.
What is the Principle Component Analysis?
As we know that the higher dimensionality of the data is a curse for the model in some ways, then it is necessary to reduce the dimensionality of the data in order to achieve higher accuracies and a reliable model; Still, we can not directly drop some of the features from the dataset as all the features can contain some values of the dataset which can not be missed.
In such cases the principle component analysis comes to the rescue; it is a technique that is used for reducing the dimensionality of the data without losing the essence of the data and without losing any of the information from the dataset.
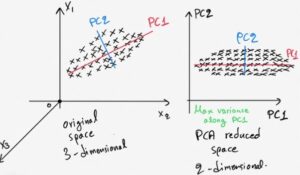
Principle component analysis or the PCA creates the principle components or vectors that represent the same data in lower dimensions, and vectors are used for training the model further.
As we can see in the above image, we have a dataset with three dimensions, X1, X2, and X3. Now here if we want to visualize the data we need to plot the data in 3 axes of the three features, but we can use principle component analysis or PCA which will reduce the dimension of the data by converting its features to only two principle components or principal vectors PC1 and PC2. Once the data is reduced to the lower dimensions now, the data can be visualized by plotting it to only two dimensions, PC1 and PC2.
How Does PCA Works?
Now that we have a core intuition about the principle component analysis, its use case, and its importance, let us discuss how this technique works and what steps are performed to reduce the dimensionality of the dataset.
Normalize the Data
The first step performed before applying the principle component analysis is to normalize the data, basically to bring the data observation values to the same scale. Although this step is not necessary, we can also directly apply PCA, but from the experiments, it is proven that applying normalization in PCA helps in many ways.
Calculate the Covariance Matrix
The next step is to calculate the covariance matrix for the datasets which will contain the information on the variance of single variables and covariance between double variables in the dataset. To compute this covariance matrix, we will take a matrix first, will transpose it, and will again multiply it by the actual matrix, which will give us the covariance matrix.
Calculate Eigen Vectors and Eigenvalues
The last step is to calculate the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the dataset, where the eigenvectors will help to decide the algorithm the best for principle components or principle vectors to select, as there can be many principle vectors possible in the dataset to reduce the dimensionality of the data.
Code Example:
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scale = StandardScaler()
X_train = scale.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scale.transform(X_test)
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components = 2)
X_train = pca.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = pca.transform(X_test)
Key Takeaways
- Curse of dimensionality is a term used when the data haves many dimensions which can increase the computational power of the model and can affect the performance of the model.
- Principle component analysis is a technique used for reducing the dimensionality of the data.
- Before calculating the vectors that represent the data in lower dimensions, it is advised to normalize the data or make the data values on the same scale.
- Principle component analysis uses the principle components or principle vectors derived from the eigenvalues and eigenvectors to reduce the dimensionality of the dataset.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the principle component analysis, the core intuition behind it, and how the principle component analysis works with code examples. This article will help one to understand the concept of principal component analysis better and will help one to apply this technique wherever necessary.